Movie recommendation system
This article is a part of a series intended to show users how to use Memgraph on real-world data and, by doing so, retrieve some interesting and useful information.
We highly recommend checking out the other articles from this series which are listed in our tutorial overview section.
Introduction
This example shows how to implement a simple recommendation system with
openCypher in Memgraph. First, we will show how to perform simple operations,
and then we will implement a query for the movie recommendation.
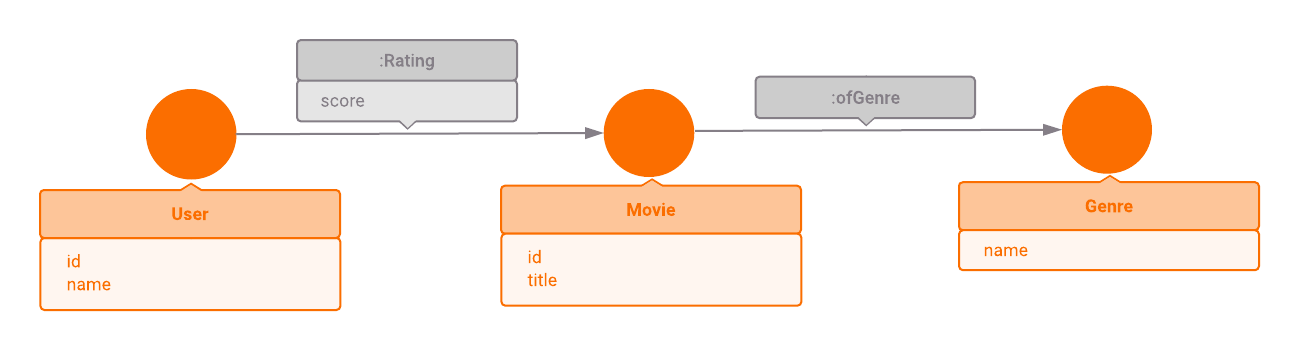
Data model
In this example, we will use reduced MovieLens dataset (less than 1000 movies).
There are three different types of data: Movie, User and Genre. Movies
have properties: id and title Users have properties: id, name Genres
have a property: name
Each movie can be connected with :ofGenre edge to different genres. A user can
rate some movie. Rating is modeled with :Rating edge and this edge has
property score — float number between 0 and 5.
Importing the dataset
To import the dataset, download the Memgraph
Lab desktop application and navigate to the
Datasets tab in the sidebar. From there, choose the dataset MovieLens:
Movies, genres and users and continue with the tutorial.
Example queries
1. List first 10 movies sorted by title
MATCH (movie:Movie)
RETURN movie
ORDER BY movie.title
LIMIT 10;
2. List last 15 users sorted by name
MATCH (user:User)
RETURN user
ORDER BY user.name DESC
LIMIT 15;
3. List 10 movies that have Comedy and Action genres and sort them by title
MATCH (movie:Movie)-[:ofGenre]->(:Genre {name:"Action"})
MATCH (movie)-[:ofGenre]->(:Genre {name:"Comedy"})
RETURN movie.title
ORDER BY movie.title
LIMIT 10;
4. Uniqueness constraint for genre:
Let's create a new unique constraint:
CREATE CONSTRAINT ON (genre:Genre) ASSERT genre.name IS UNIQUE;
And now we can try to create new Genre node with existing `name': "Comedy":
CREATE (:Genre {name: "Comedy"});
This query returns an error because genre "Comedy" already exists.
5. Average score for Star Wars movie:
MATCH (:User)-[rating:Rating]->(:Movie {title:"Star Wars"})
RETURN avg(rating.score);
6. Average scores for first 10 movies:
MATCH (:User)-[:Rating]->(movie:Movie)
RETURN movie.title, avg(r.score) AS score
ORDER BY score DESC
LIMIT 10;
7. Create a new user and rate some movies:
CREATE (:User {id:1000, name:"Aladin"});
Check if new user is created:
MATCH (user:User{name:"Aladin"})
RETURN user;
Rate some movies:
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Trois couleurs : Rouge"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"20,000 Leagues Under the Sea"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:1.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Star Trek: Generations"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:0.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Rebecca"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"The 39 Steps"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:4.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Faster, Pussycat! Kill! Kill!"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Once Were Warriors"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Sleepless in Seattle"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:4.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Don Juan DeMarco"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:4.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Jack & Sarah"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:1.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Mr. Holland's Opus"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:2.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"The Getaway"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Color of Night"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:4.0}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Reality Bites"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:2.5}]-(m);
MATCH (u:User {id:1000}), (m:Movie {title:"Notorious"})
MERGE (u)-[:Rating {score:3.5}]-(m);
8. Recommendation system:
The idea is to implement simple memory based collaborative filtering.
Let's recommend some movies for user Aladin:
MATCH (u:User {id:1000})-[r:Rating]-(m:Movie)
-[other_r:Rating]-(other:User)
WITH other.id AS other_id,
avg(abs(r.score-other_r.score)) AS similarity,
count(*) AS similar_user_count
WHERE similar_user_count > 2
WITH other_id
ORDER BY similarity
LIMIT 10
WITH collect(other_id) AS similar_user_set
MATCH (some_movie: Movie)-[fellow_rate:Rating]-(fellow_user:User)
WHERE fellow_user.id IN similar_user_set
WITH some_movie, avg(fellow_rate.score) AS prediction_score
RETURN some_movie.title AS Title, prediction_score
ORDER BY prediction_score DESC;
How does this query work?
This query has two parts:
- Finding similar users
- Predicting the score for some movie (recommendation)
In the first part, we are looking for similar users. First, we need to define similar users: Two users are considered similar if they tend to give similar scores to the same movies. For the target user (Aladin) and some other user we are searching for the same movies:
MATCH (u:User {id:1000})-[r:Rating]-(m:Movie)-[other_r:Rating]-(other:User);
But this is not enough for finding similar users. We need to choose users with the same movies and similar scores:
WITH other.id AS other_id,
avg(abs(r.score-other_r.score)) AS similarity,
count(*) AS similar_user_count
WHERE similar_user_count > 2
WITH other_id
ORDER BY similarity
LIMIT 10;
Here we calculate similarities as the average distance between target user score and some other user score on the same set of movies. There are two parameters: similarUserCount limit (2) and similar user set size limit (10). Similar user count limit is used for filtering users who have at least 2 movies in common with the target user. Similar user set size is used to peek top 10 similar users (10 or less).
Now we have similar user set. We will use those users to calculate the average score for all movies in the database.
MATCH (some_movie: Movie)-[fellow_rate:Rating]-(fellow_user:User)
WHERE fellow_user.id IN similar_user_set
WITH some_movie, avg(fellow_rate.score) AS prediction_score
RETURN some_movie.title AS title, prediction_score
ORDER BY prediction_score DESC;
We encourage you to play with some parameters, like similar user count limit and similar user set size limit. You can also try to use different similarity functions, for example Euclidean distance:
sqrt(reduce(a=0, x IN collect((r.score - other_r.score) * (r.score - other_r.score)) | a + x)) AS similarity;
Here we use reduce function. Reduce function accumulate list elements into a
single result by applying an expression. In our query, this function starts with
0 and sums up squared differences. collect function is used for putting
squared differences into the list.